Democracy in Norway

Watch the film
Democracy in Norway

The central government, county authorities and municipalities
- There are 15 counties and 357 municipalities in Norway (01.01.2025).
- Counties and municipalities are both geographical areas and administrative units subject to political control.
- Both the county authorities and the municipalities are self-governing in certain areas, even though the central government decides many things.
- The central government sets the framework for the counties and municipalities.
- The central government rules the whole country, while the county and municipal authorities only decide local issues.
Some of the central government's areas of responsibility:
- foreign policy
- hospitals
- laws
- school curricula
Some of the county authorities’ areas of responsibility:
- upper secondary education
- county roads


Some of the municipalities’ areas of responsibility:
- primary and lower secondary schools
- kindergartens
- care for the elderly
- refuse collection, water and sewerage
- municipal roads


Political and administrative control
The central government and the counties and municipalities are governed by politicians elected by the people. This means that politicians discuss issues and decide on a policy for different areas. But it is the civil servants in the public administration – state, county authority and municipal staff – who implement the policies.
Examples:
- Politicians adopt school curricula. Teachers teach in accordance with these curricula.
- Politicians adopt rules for the payment of social security benefits. NAV employees must comply with these rules.
The Storting
Norway's parliament is called the Storting. It has 169 members elected by the people for a term of four years. The members represent different political parties. The Storting is the supreme branch of government in Norway.
The Storting’s most important functions:
- to adopt new laws and amend old ones
- to adopt the national budget
- to oversee the government and the central government administration
- to debate political issues and major projects
Norway has an open democracy. Everyone who wants to can attend the Storting and listen to the politicians debating different issues. However, the public does not have the right to speak or make statements about matters in the Storting. Many matters are distributed for consultation. This gives experts and ordinary people the chance to have a say.

The government
After a general election, one or several parties form a new government. The government consists of the ministers (the political heads of each ministry) and the prime minister. One of the government's functions is to propose new laws and amend existing legislation, but the Storting adopts the laws and legislative amendments. The government is tasked with ensuring that the decisions of the Storting are implemented in practice. The government also prepares a national budget proposal every year.
Council of State
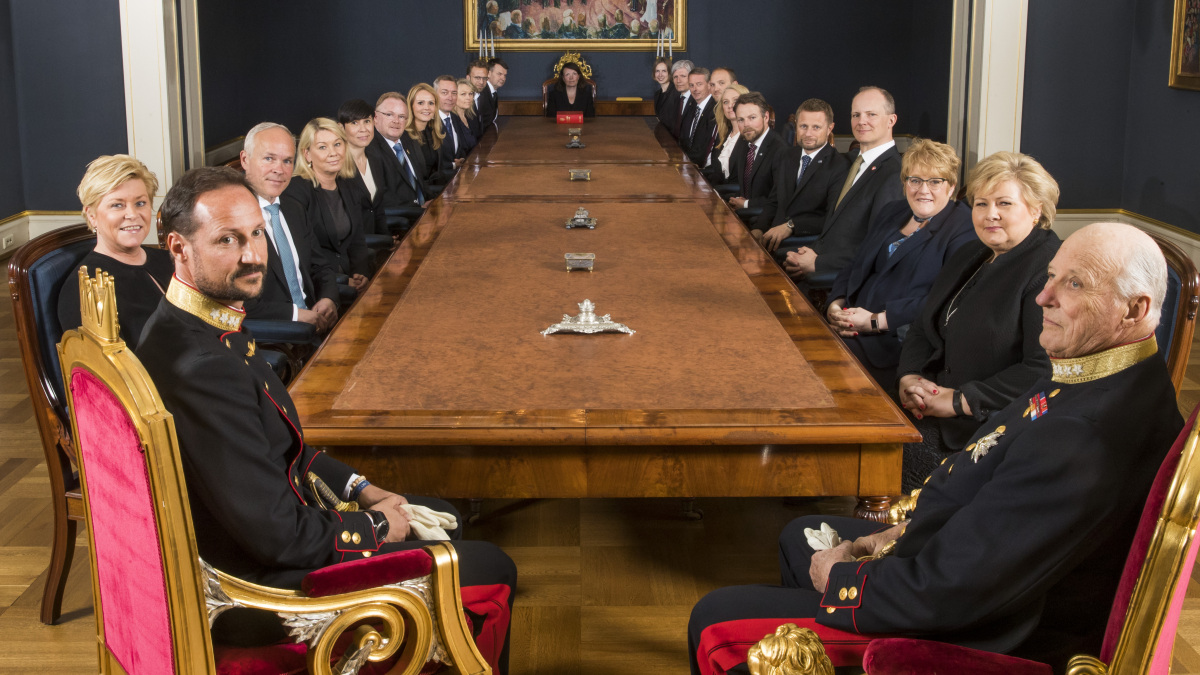

The government has a meeting with the King every Friday. At these meetings, the ministers inform the King about different political matters. This meeting is called the Council of State. The King does not have much political power, but these meetings are nevertheless important.
The principle of separation of powers
Separation of powers means that power is divided between three independent branches of government:
- A legislative branch – the Storting – which adopts laws.
- An executive branch – the government – which proposes laws and ensures that they are implemented.
- A judiciary branch – the courts of law – that pass judgment in court cases in accordance with the legislation adopted by the Storting.
When powers are divided between these three branches of government, none of them can have too much power. This thus secures democracy.
Talk together

- Talk about the governing bodies in countries you know of.
- Discuss the separation of power in Norway
- Discuss the central government’s, counties’ and municipalities’ tasks in a welfare society.
- How can you influence the society you live in?
- Do you think it is easier to influence local rather than national matters? Why or why not?

Select the right answer
Which of the alternatives fall under the central government’s areas of responsibility?
Select the right answer
What is Norway’s parliament called?
Select the right answer
What is a Council of State?
Select right or wrong
Read the statements. What is right? What is wrong?
Select right or wrong
Read the statements. What is right? What is wrong?
